2D-3D Tooth Imaging
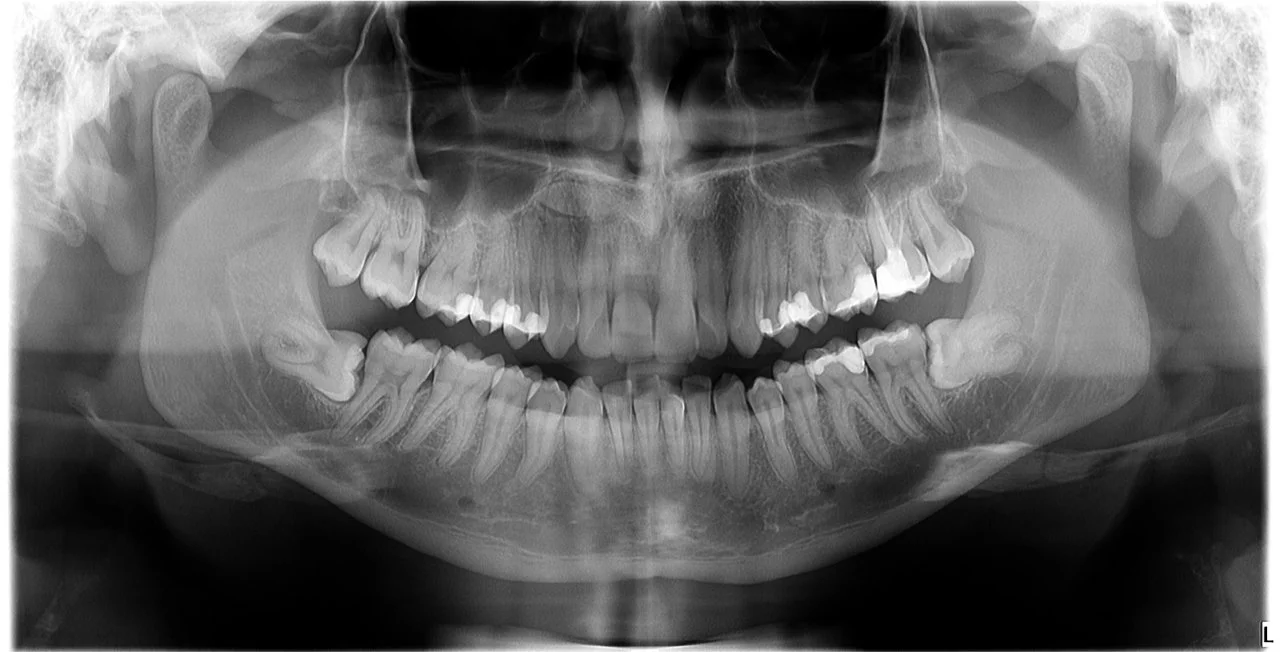
2D-3D Tooth Imaging refers to the use of technology that enables the creation of three-dimensional images (3D) of teeth, jaws, and surrounding structures. This advanced approach in dentistry provides more precise information about oral health compared to traditional two-dimensional (2D) X-ray images.
- 2D X-ray Images: Traditional X-ray images provide two-dimensional pictures, which can limit the dentist’s ability to accurately assess the three-dimensional structure of teeth and surrounding tissues.
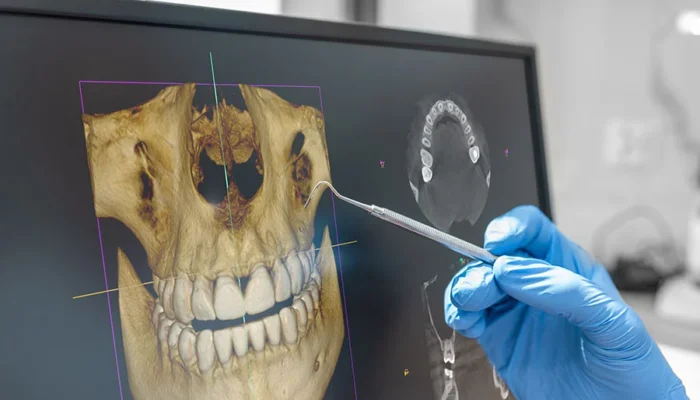
- 3D X-ray Images (CBCT): Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) is a technology that allows the generation of three-dimensional images of the oral region. This technique uses cone-shaped X-rays, enabling more precise and detailed imaging.
- Advantages of 3D Imaging:
- Precision: 3D imaging provides more detailed information about the structure of teeth, bone, and soft tissues.
- Planning: Used in planning oral surgical procedures, such as implant placement or tooth extraction.
- Diagnosis: Assists in the diagnosis and monitoring of oral diseases, infections, tumors, and other pathologies.
- Individualized Treatment: Allows the dentist to customize treatment based on precise data.
- Applications of 2D-3D Imaging:
- Implant Placement: Precise planning of implant positions.
- Oral Surgery: Planning oral surgical procedures.
- Orthodontics: Assessment of tooth and bone positions for orthodontic treatment.
- Diagnosis: Detailed analysis of the condition of teeth, bone, and soft tissues.
- Safety and Radiation Dosage: Although it provides detailed information, CBCT uses less radiation compared to traditional CT scanners.
- 2D-3D tooth imaging plays a crucial role in modern dentistry, allowing dentists to provide more precise diagnostic information and individualized treatment approaches. This technological advancement contributes to more efficient and safer dental care delivery.